过去完成时的用法 正确运用过去完成时的方法
过去完成时通常表述的是过去某一时刻前发生的动作或者存在的状态,其用法你了解多少呢?以下是由小编整理关于过去完成时的用法的内容,希望大家喜欢!
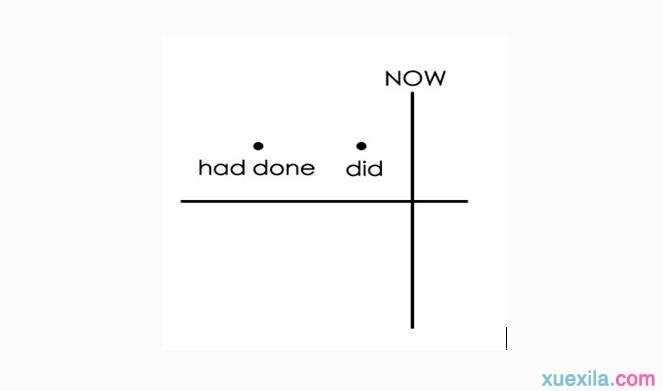
过去完成时的用法
1、定义
①表示发生在过去的动作对过去晚些时候造成的影响或结果
②过去某一动作一直持续到过去晚些时候将来可能还要延续。
句中的动作发生在过去之前(过去的过去),即过去完成时动作发生在过去的过去。
He said he had been to Beijing twice. 他说他已经去过北京两次。(因为“说”said就是过去式,而去北京的动作发生在说said 的过去,所以用过完而不用现完。
过去完成时常用的时间状语有
(1)、by the end of last year. By the end of last term, we had learned 5000 new words.
(2)、By the time sb. +动词过去式 The bus had already left by the time I got there.
2、基本结构
主语+had+过去分词vpp.(done)
①肯定句:主语+had+过去分词.
②否定句:主语+had+not+过去分词.
③一般疑问句:Had+主语+过去分词? 肯定回答:Yes,主语+had. 否定回答:No,主语+had not . ④特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词或词组+一般疑问句(Had+主语+过去分词)?
⑤被动语态:主语+had(hadn't)+been+过去分词
3、基本用法
(1)表示在过去某一时刻或动作以前完成了的动作,也可以说过去的时间关于过去的动作。即“过去的过去”。可以用by, before等介词短语或一个时间状语从句 (在复合句中,由时间连接词引导的状语从句叫做时间状语从句 )来表示,也可以用一个表示过去的动作来表示,还可能通过上下文来表示。例如:By nine o’clock last night, we had got 200 pictures from the spaceship.
(2)表示由过去的某一时刻开始,一直延续到过去另一时间的动作或状态,常和for, since构成的时间状语连用。例如:I had been at the bus stop for 20 minutes when a bus finally came./He said he had worked in that factory since 1949.
(3)叙述过去发生的事情,在已叙述了过去发生的事情后,反过来追述或补述以前发生的动作时,常使用过去完成时。例如:Mr. Smith died yesterday. He had been a good friend of mine./ I didn’t know a thing about the verbs, for I had not studied my lesson.
(4)在含有定语从句的主从复合句中,如果叙述的是过去的事,先发生的动作常用过去完成时。 例如:I returned the book that I had borrowed./ She found the key that she had lost.
(5)过去完成时常常用在told,said,knew,heard,thought等动词后的宾语从句(或间接引语)中,这时从句中的动作发生在主句表示的过去的动作之前。例如:He said that he had known her well./ I thought I had sent the letter a week before.
(6)状语从句:在过去不同时间发生的两个动作中,发生在前,用过去完成时;发生在后,用一般过去时。如when,before,after,as soon as,till/until引导的。例如:When I woke up, it had already stopped raining./ She didn’t go to bed until she had finished her work.
注意:如果两个动作紧接着发生,则常常不用过去完成时,特别是在包含before和after的复合句中,因为 这 时从句的动作和主句的动作发生的先后顺序已经非常明确,这时可以用一般过去时代替过去完成时。例如:After he arrived in England, Marx worked hard to improve his English.
(7)动词think, want, hope, mean, plan, intend等用过去完成时来表示过去未曾实现的想法,希望,打算或意图等。例如:They had wanted to help but could not get there in time./ We had hoped to be able to come and see you .
(8)过去完成时还可用在hardly…when…, no sooner…than…, It was the first (second, etc) time (that) … 等固定句型中。例如:Hardly had he begun to speak when the audience interrupted him./ No sooner had he arrived then he went away again./ It was the third time that he had been out of work that year.
时间状语before,when,after,by+,until, once,had no sooner……than,yet,already等。
3、过去完成时-语法判定
A、由时间状语来判定。一般说来,各种时态都有特定的时间状语。与过去完成时连用的时间状语有:
( 1 ) by + 过去的时间点。如:I had finished reading the novel by nine o'clock last night.
( 2 ) by the end of + 过去的时间点。如: We had learned over two thousand English words by the end of last term.
( 3 ) before + 过去的时间点。如:They had planted six hundred trees before last Wednesday.
B、由“过去的过去”来判定。过去完成时表示“过去的过去”,是指过去某一动作之前已经发生或完成的动作,即动作有先后关系,动作在前的用过去完成时,在后的用一般过去时。这种用法常出现在:
( 1 )宾语从句中,当宾语从句的主句为一般过去时,且从句的动作先于主句的动作时,从句要用过去完成时。在told, said, knew, heard, thought等动词后的宾语从句。如:She said that she had seen the film before.
( 2 )状语从句中,在时间、条件、原因、方式等状语从句中,主、从句的动作发生有先后关系,动作在前的,要用过去完成时,动作在后的要用一般过去时。如:After he had finished his homework, he went to bed. 注意: before, after 引导的时间状语从句中,由于 before 和 after 本身已表达了动作的先后关系,若主、从句表示的动作紧密相连,则主、从句都用一般过去时。如:After he closed the door, he left the classroom.
( 3 )表示意向的动词,如hope, wish, expect, think, intend, mean, suppose等,用过去完成时表示"原本…,未能…" We had hoped that you would come, but you didn't.
C、根据上、下文来判定。I met Wang Tao in the street yesterday. We hadn't seen each other since he went to Beijing.
4、过去完成时-语法区别
(1)、过去完成时与现在完成时的区别
现在完成时表示的动作发生在过去,以现在的时间为基点,但侧重对现在产生的结果或造成的影响,与现在有关,其结构为“助动词 have (has) + 过去分词”;过去完成时则是一个相对的时态,以过去时间为基点,它所表示的动作不仅发生在过去,更强调“过去的过去”,只有和过去某时或某动作相比较时,才用到它。
比较:I have learned 1000 English words so far.到目前为止我已经学会了 1000 个英语单词。
I had learned 1000 English words till then.到那时为止我已经学会了 1000 个英语单词。
— I'm sorry to keep you waiting. 对不起,让你久等了。
— Oh, not at all. I have been here only a few minutes.没什么,我只等了几分钟。(“等”的动作从过去某一时间点持续到现在)
(2)、过去完成时与一般过去时的区别
虽然这两种时态都表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态,但在使用时应注意以下几点:
A. 时间状语不同:过去完成时在时间上强调“过去的过去”;而一般过去时只强调过去某一特定的时间。
比较:They had arrived at the station by ten yesterday.
They arrived at the station at ten yesterday.
B. 在没有明确的过去时间状语作标志时,谓语动词动作发生的时间先后须依据上下文来判断:先发生的用过去完成时,后发生的则用一般过去时。She was very happy. Her whole family were pleased with her, too. She had just won the first in the composition competition.
C. 当两个或两个以上接连发生的动作用 and 或 but 连接时,按时间顺序,只需用一般过去时来代替过去完成时;另外,在 before , after , as soon as 引导的从句中,由于这些连词本身已经表示出时间的先后,因此也可以用过去时来代替过去完成时。 He entered the room, turned on the light and read an evening paper.
如何正确运用过去完成时
1. 正确运用过去完成时最重要的是要正确理解“过去的过去”。“过去的过去”是一个相对时间,即它相对于一个过去时间而言,并在其过去。这种相对的“过去的过去”有时通过一定的时间副词(状语)体现出来,有时则可能是通过一定的上下文来体现:
I found the watch which I had lost.
我找到了我丢失的表。
The house was quiet. Everybody had gone to bed.
屋子里很安静,大家都睡觉了。
"Was Jack at the office?" "No, he’d gone home." “杰克在办公室吗?”“不在,回家了。”
【注】有些通常与现在完成时连用的词语,由于在一定的语境中,谓语动作移到了“过去的过去”,也应用过去完成时。比较:
We haven’t seen each other since we left Paris.
自从离开巴黎后我们一直没见过面。
I saw Mr Smith last Sunday. We hadn’t seen each other since we left Paris.
一般过去时的用法
上周星期天我见到史密斯先生了,自从离开巴黎后我们还一直没见过面。
2. 表示过去未曾实现的想法
过去完成时可表示过去未曾实现的想法和打算,通常连用的动词是 want, think, hope, plan, mean, expect, intend, suppose 等:
I had meant to come, but something happened.
我本想来,但有事就没有来。
I had intended to speak, but time did not permit.
我本想发言,但时间不允许。
We had hoped that you would come to see us, but you didn’t.
我们本想你来看我们的,但你没有来。